Tips For Better Living In An Open-Plan Space
What Is Radiations
Radiation, a phenomenon often encountered but not fully understood, is the focus of this article.
In a technical, precise, and research-oriented style Lead glass radiation, we delve into the basics of radiation, including its types and measurement.
With an emphasis on understanding radiation exposure, we explore its applications in everyday life.
This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview, catering to an audience seeking knowledge and freedom to make informed choices regarding radiation and its implications.
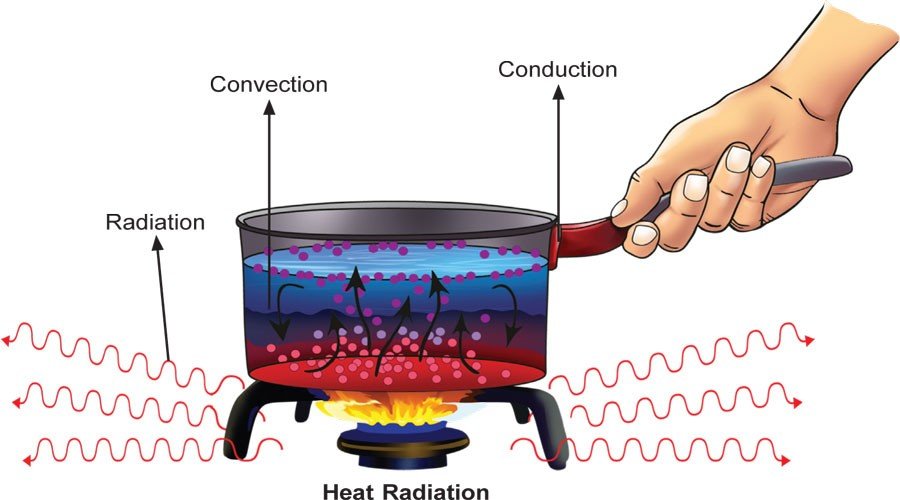
The Basics of Radiation
Radiation is a form of energy that is emitted in the form of waves or particles. It is a fundamental concept in physics and plays a crucial role in various scientific and technological applications.
Understanding the effects of radiation and ensuring radiation safety is of utmost importance lead sheet supplier Malaysia. Exposure to high levels of radiation can have detrimental effects on living organisms, including damage to DNA, increased risk of cancer, and radiation sickness. Therefore, it is essential to establish and adhere to strict safety guidelines when working with radiation sources.
These guidelines typically include measures such as proper shielding, minimizing exposure time, and maintaining safe distances from radiation sources. Additionally, regular monitoring and assessment of radiation levels are critical to ensure a safe environment for individuals who may be exposed to radiation.
Types of Radiation
There are various types of electromagnetic waves that fall within the range of ionizing radiation, such as X-rays and gamma rays. These types of radiation are commonly used in radiation therapy, a medical treatment that uses high-energy radiation to target and destroy cancer cells.
Radiation therapy plays a crucial role in cancer treatment, offering a non-invasive alternative to surgery. However, it is important to ensure radiation safety during these procedures. Radiation safety measures include shielding and monitoring devices, as well as strict adherence to dosage guidelines.
Additionally, proper training and certification of medical professionals involved in radiation therapy are essential to ensure the safe and effective delivery of treatment. By prioritizing radiation safety, healthcare providers can minimize the risks associated with ionizing radiation and maximize the benefits for patients.
Measuring Radiation Levels
One of the key aspects in radiation safety is accurately measuring the levels of electromagnetic waves emitted during radiation therapy procedures. Radiation detection and monitoring play crucial roles in ensuring the well-being of both patients and healthcare providers.
To measure radiation levels, various types of detection devices are used, such as ionization chambers, solid-state detectors, and scintillation detectors. These devices are designed to detect different types of radiation, including alpha particles, beta particles, gamma rays, and X-rays. They work by converting the energy of the radiation into measurable signals, which can then be used to determine the intensity and type of radiation present.
Regular monitoring of radiation levels is important to identify any deviations from safe levels and to ensure that appropriate safety measures are in place. By using reliable and accurate radiation detection and monitoring techniques, the risks associated with radiation exposure can be minimized, providing a safer environment for all involved.

Understanding Radiation Exposure
To fully comprehend the potential health risks associated with radiation exposure, it is crucial to have a comprehensive understanding of the various factors that contribute to the overall dose received by an individual. Radiation safety is of paramount importance in order to minimize these risks.
Exposure to ionizing radiation can have both immediate and long-term health effects. Acute effects include radiation sickness, which can lead to nausea, vomiting, and even death in severe cases. Chronic effects, on the other hand, may manifest years or even decades after exposure and can include an increased risk of developing cancer or genetic mutations.
The health effects of radiation exposure are dependent on several factors, including the type and energy of radiation, the duration and frequency of exposure, and individual susceptibility. Understanding these factors is essential in developing effective safety measures and guidelines to protect individuals from the harmful effects of radiation exposure.
Applications of Radiation in Everyday Life
Radiation is utilized in various applications in our daily lives, such as medical imaging, nuclear power generation, and food sterilization.
One significant application of radiation is in the field of medicine, specifically in radiation therapy. Radiation therapy is a commonly used treatment for cancer, where high-energy radiation is directed at the tumor to kill cancer cells or prevent their growth. This therapy offers several benefits, including targeted treatment, minimal invasiveness, and the ability to preserve healthy tissues surrounding the tumor.
Radiation also plays a crucial role in food preservation. By exposing food to ionizing radiation, the growth of bacteria, viruses, and parasites can be inhibited, extending the shelf life of perishable items. This method is particularly useful in preventing foodborne illnesses and reducing food wastage. Furthermore, radiation can control insect infestations, delay ripening, and inhibit sprouting in fruits and vegetables, ensuring their quality and safety.
However, it is important to note that regulatory authorities closely monitor the use of radiation in food preservation to ensure the safety and efficacy of the process.
Conclusion
In conclusion, radiation refers to the emission of energy in the form of particles or electromagnetic waves. It can be classified into different types, such as ionizing and non-ionizing radiation, each with varying levels of intensity and potential health risks.
Radiation levels are measured using specialized instruments, and understanding exposure is crucial in assessing its impact on human health.
Moreover, radiation finds applications in various fields, including medicine, industry, and telecommunications, highlighting its significance in everyday life.

